In emergencies, seconds matter. The simple nasal spray delivery of neffy is designed to reduce hesitation and error. The choice is yours.
Real-world data
Real patients.
Real anaphylaxisReal results
First large-scale (N=680) survey of real-world outcomes with neffy during anaphylaxis events1
Key findings1
- Approximately 9 in 10 patients (88.7%) experiencing anaphylaxis during oral food challenge or allergen immunotherapy were successfully treated with a single dose of neffy administered by a healthcare provider.
- Real-world effectiveness is consistent with historic success rates for epinephrine injection (88.9%).2
- Growing data supports evidence-based prescribing and optimal patient care.
- Survey highlights real-world use of neffy in anaphylaxis management.
Real-world anaphylaxis treatment success rate with a single dose of epinephrine1
Historical control treatment success rate with a single dose of epinephrine2
Note: Not a head-to-head trial; comparator is historical literature. Real-world observational data have inherent limitations.1
About the study1
Data source: neffy Experience Program—retrospective analysis of treatments by 375 healthcare providers; survey conducted by ARS Pharma
Population: Of the 2947 participating HCPs, 375 reported treating a total of 680 patients with neffy; 603 patients (88.7%) were effectively treated with a single dose; 77 patients (11.3%) required a second dose of epinephrine, which is consistent with historical literature on food-induced anaphylaxis (11.1%)
Safety: The most commonly reported adverse events (≥1%) were headache, nasal discomfort, rhinalgia, and epistaxis. Adverse events were spontaneously reported and not systematically collected
Setting: Anaphylaxis during oral food challenge or allergen immunotherapy
Publication: Peer-reviewed publication in Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (official journal of the ACAAI)
Limitations: This study was a non-controlled survey. There was also potential for recall bias because outcomes were self-reported; as-observed data may bias results. Safety and tolerability data were not collected
Note: Not a head-to-head trial; comparator is historical literature. Real-world observational data have inherent limitations.1
ACAAI, American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology; HCP, healthcare provider; IM, intramuscular injection.


“The finding that about 9 out of every 10 patients were successfully treated with a single dose of neffy is essentially identical to the historic response rates observed with epinephrine injection.”
— Dr Thomas B. Casale, University of South Florida“Findings from this real-world report align with the positive impact that I have seen firsthand in my own patients treated with neffy.”
— Dr Jonathan M. Spergel, MD, PhD, Professor of Pediatrics and Chief of the Allergy Program at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia
PD data
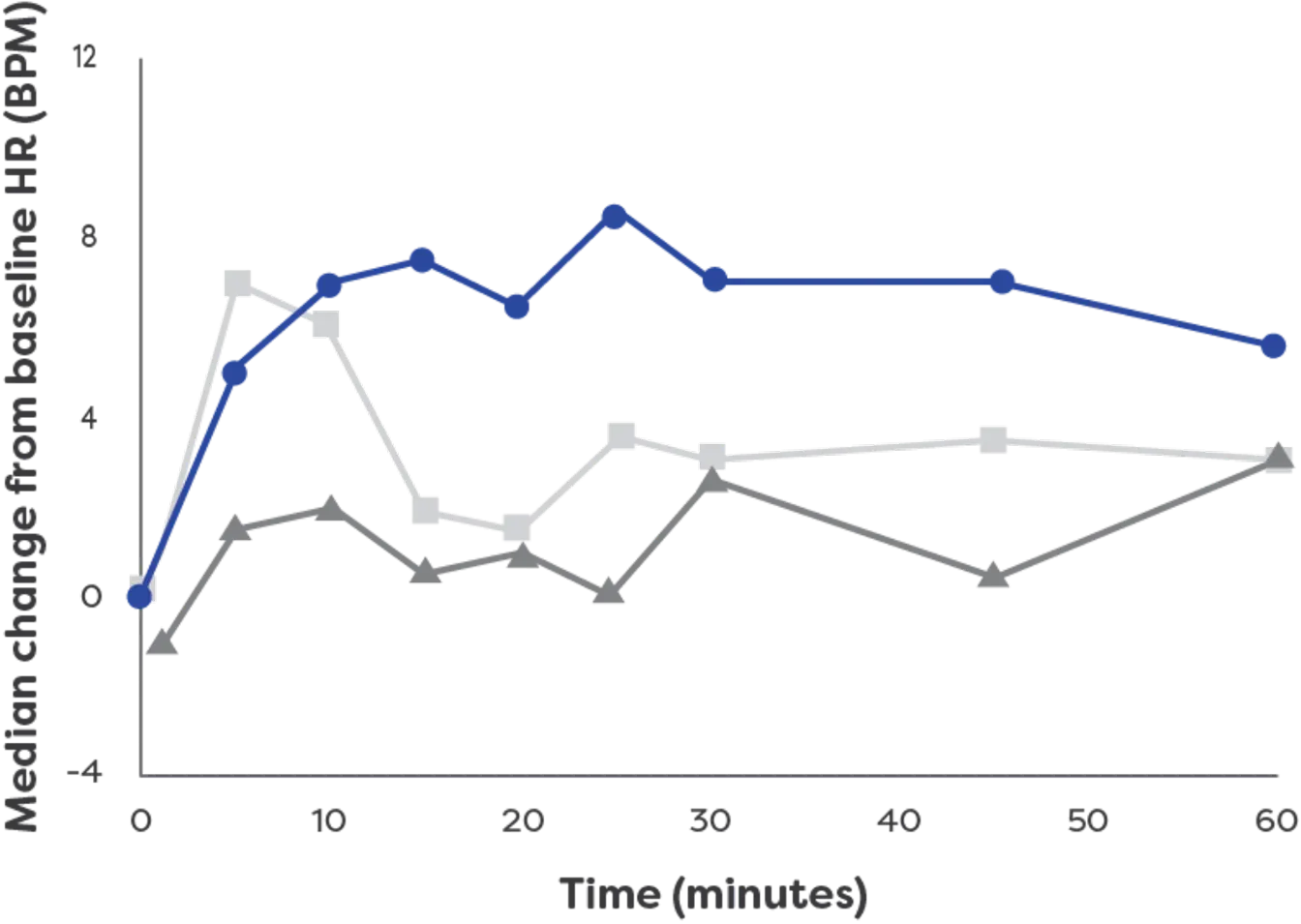
neffy has a rapid effect on heart rate3*†
Effects on heart rate by
epinephrine treatment (After 1 dose)3
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
neffy had an effect on heart rate within 1 minute
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
*The clinical meaning of PD responses observed in healthy subjects is unclear in the context of treating anaphylaxis.3
†PD analysis of a single dose of neffy
BPM, beats per minute; HR, heart rate; IM, intramuscular; PD, pharmacodynamic.
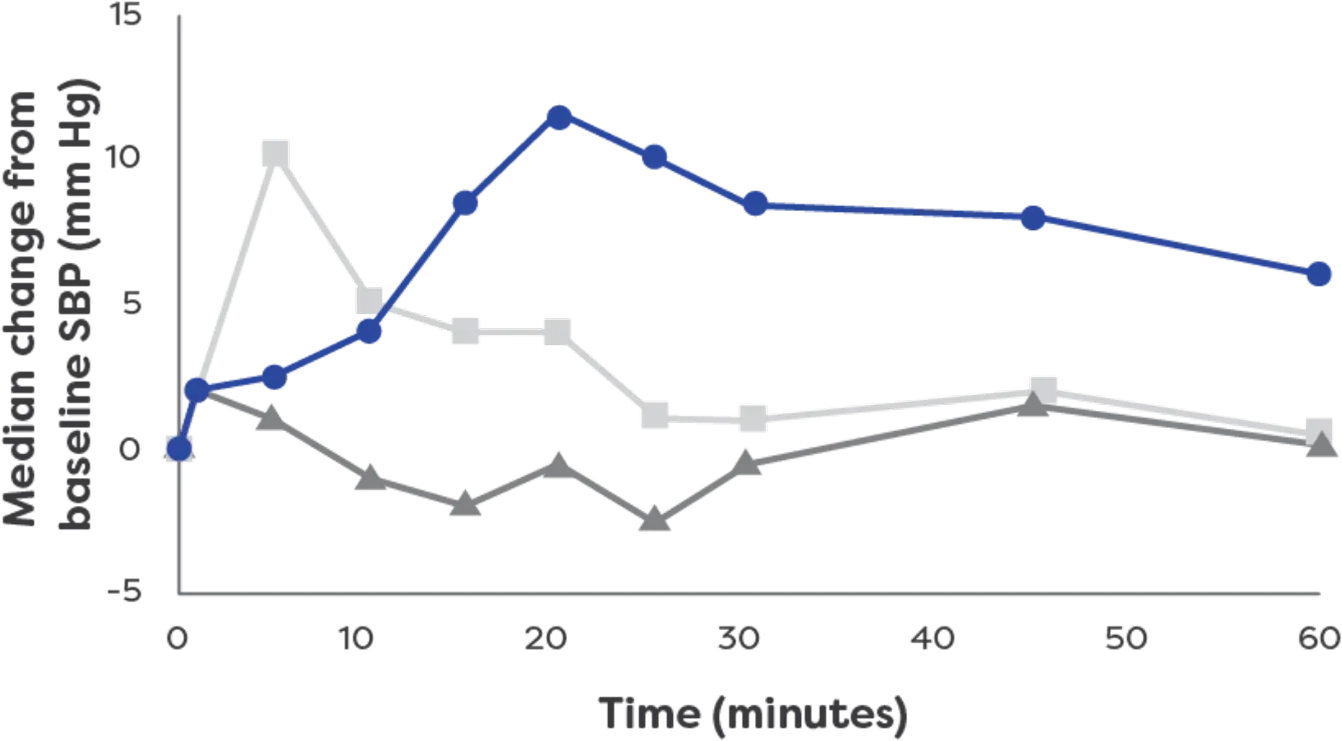
neffy has a rapid effect on systolic blood
pressure3*†
Effects on systolic blood pressure
by epinephrine treatment (After 1 dose)3
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
neffy had an effect on systolic blood pressure
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
*The clinical meaning of PD responses observed in healthy subjects is unclear in the context of treating anaphylaxis.3
†PD analysis of a single dose of neffy 2.0 mg compared to
mm Hg, millimeters of mercury; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
Oral food challenge
100% of patients achieved symptom resolution with 1 dose4‡
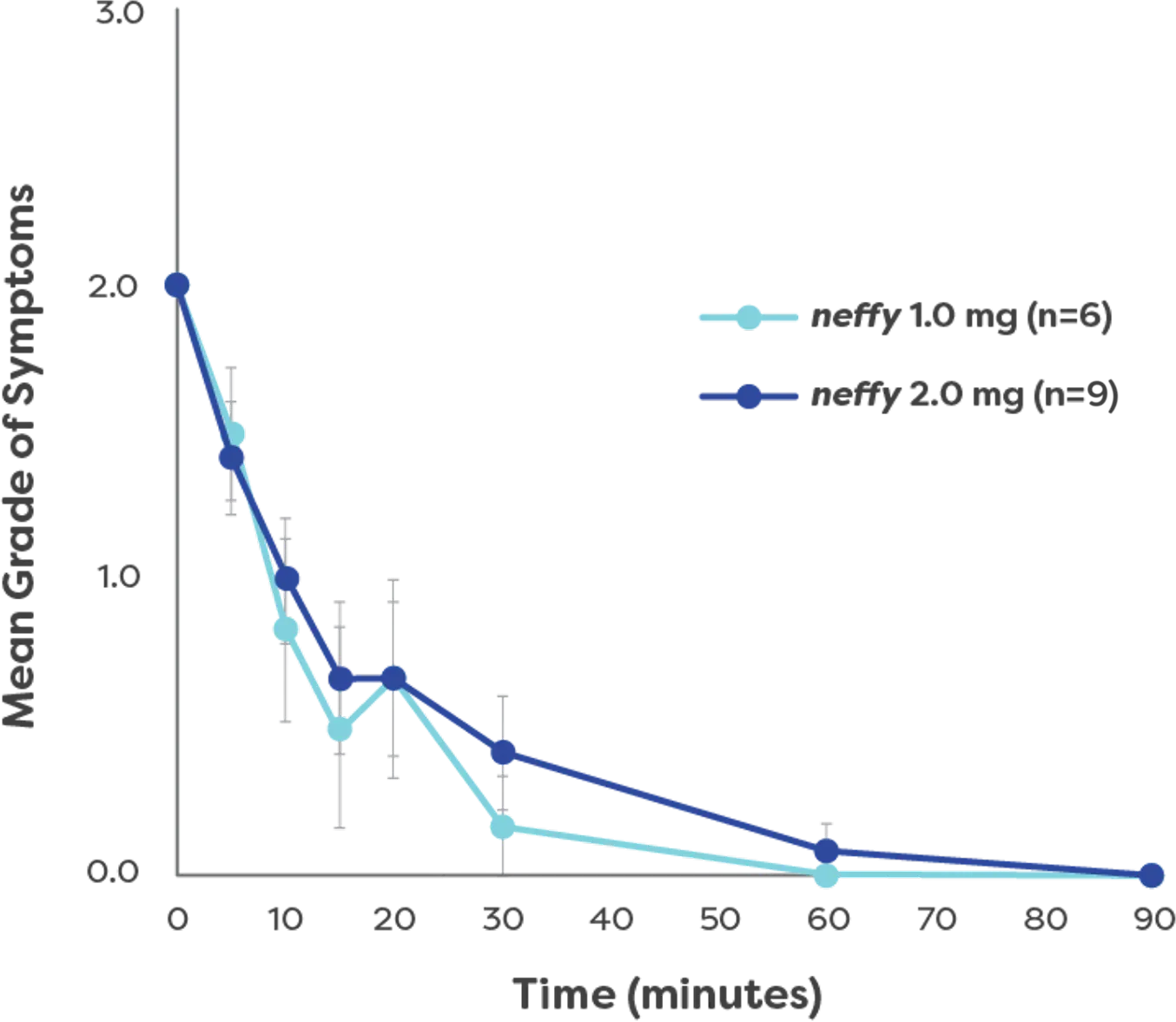
- Patients had symptom relief as early as 5 minutes4
- Symptoms resolved in a median time of 16 minutes4
- neffy was demonstrated to be safe and tolerable with no serious adverse events observed during the study4,5
‡One patient developed a biphasic reaction 2 hours and 45 minutes following administration of neffy and was treated with epinephrine at the time of that reaction.4,5
Simulating real-world type I allergic
reactions with OFC
Overview:
This Phase 3, open-label study evaluated the efficacy and safety of a single dose of neffy (
- Clinical symptoms (skin/mucosa, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nerves) were induced via OFC and graded per the Anaphylaxis Guideline4
- neffy was administered based on weight: 15 to <30 kg:
1.0 mg; ≥30 kg: 2.0 mg4
Patients:
- 15 Japanese pediatric patients (ages 6–17) with confirmed food allergy reactions (Grade 2+ in gastrointestinal, respiratory, or circulatory symptoms)4
Endpoints:
Primary endpoint4:
- Improvement rate from baseline at 15 minutes or before alternative treatment*
(Main symptom prioritization: cardiovascular > respiratory > gastrointestinal)
Selected secondary endpoints4:
- Patients not requiring alternative treatment
- Symptom grade over time
- Time to resolution by organ system
*Improvement was defined as a decrease in the grade of each organ symptom by 1 or more compared to the pre-dose grade.4
Foods that were determined or suspected to be a causative allergen were divided into single doses or multiple doses and were recorded (ie, chicken egg, wheat, milk, peanut, cashew nut, walnut, soba, etc).4
OFC, oral food challenge.
Mild (Grade 1)
- Localized redness, itching, or swelling (lip/eyelid)
- Mild stomach pain, nausea, or single vomiting
- Intermittent cough, nasal congestion, sneezing
Moderate (Grade 2)
- Generalized redness, severe itching, face swelling
- Severe stomach pain, repeated vomiting/diarrhea
- Repetitive cough, wheezing, mild dizziness
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia), mild low blood pressure
Severe (Grade 3) – EMERGENCY
- Widespread swelling, trouble breathing, hoarseness
- Continuous vomiting, loss of bowel control
- Severe wheezing, difficulty swallowing, throat tightness, cyanosis
- Severe low blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, cardiac arrest
- Anxiety, fainting, loss of consciousness
Rhinitis data
neffy pharmacokinetic data
neffy remained effective even
in patients with rhinitis3*†
Epinephrine plasma concentration-time profiles following 1 or 2 dose(s) in healthy adults with and without NAC-induced rhinitis3
Mean Epinephrine Concentration: Single Dose3
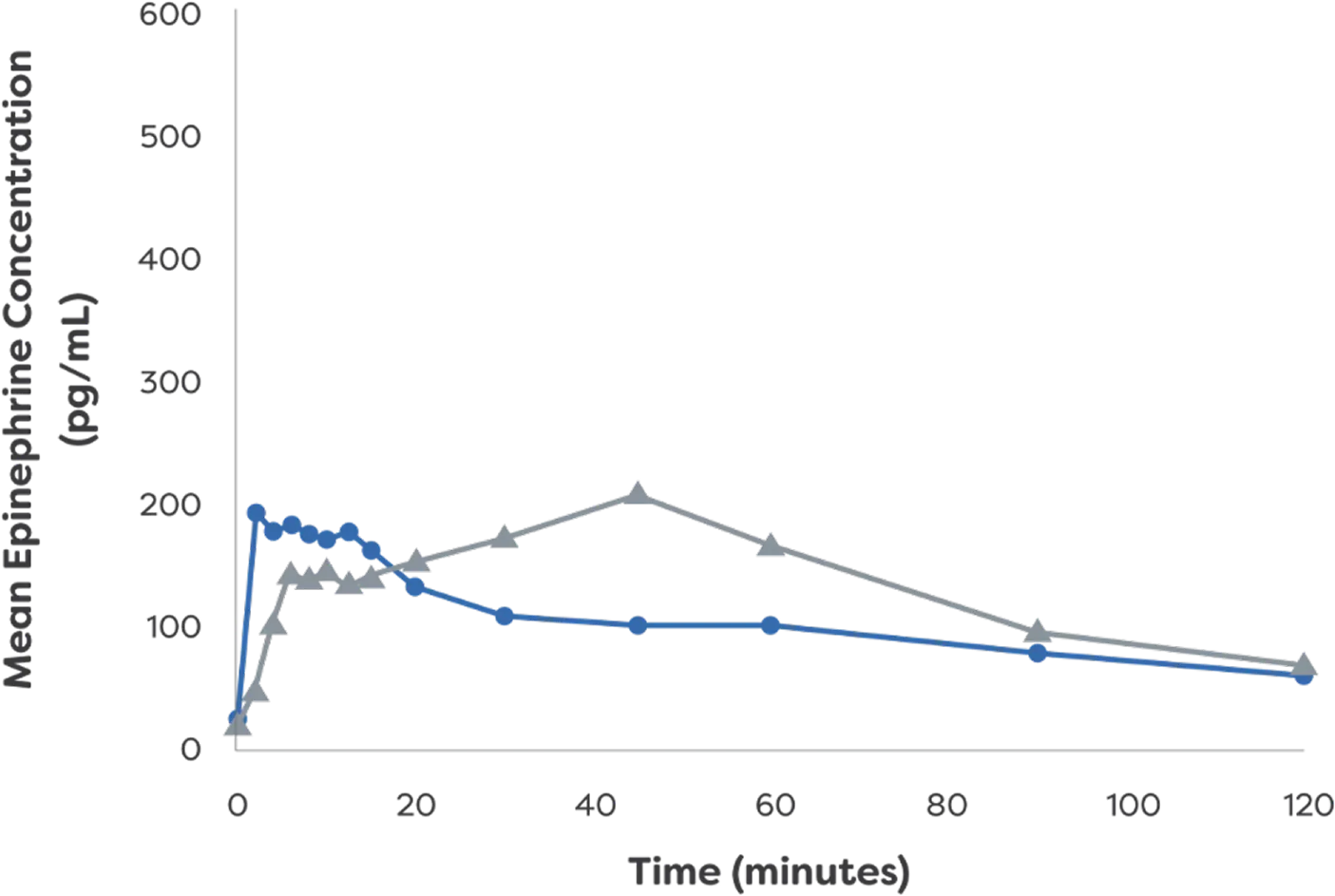
- neffy 2.0 mg
(with NAC) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe)
Mean Epinephrine Concentration: Twice Dose3
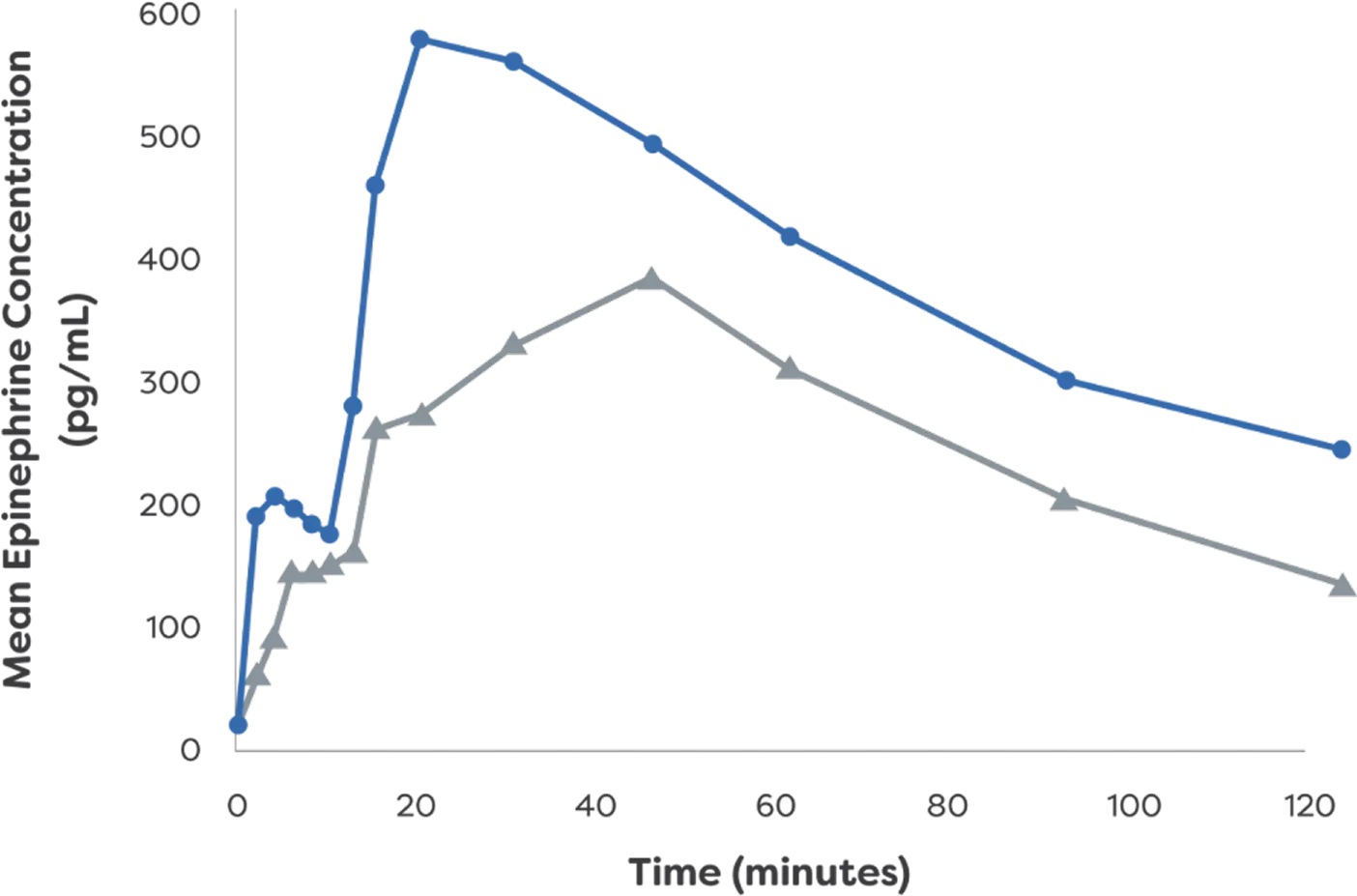
- neffy 2.0 mg
(with NAC) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe)
*PK data are not indicative of efficacy and the clinical significance is not known.3
†Study analyzed PK and PD of neffy
IM, intramuscular; NAC, nasal allergen challenge; PD, pharmacodynamic; pg/mL, picograms per milliliter; PK, pharmacokinetic.
Safety data
neffy was well tolerated in a robust clinical study program3
| Common adverse reactions in primary studies3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse reaction* | neffy 2.0 mg | neffy 2.0 mg |
| Throat irritation | 2% | 19% |
| Headache | 6% | 18% |
| Nasal discomfort | 10% | 13% |
| Feeling jittery | 1% | 11% |
| Tremor | 0% | 8% |
| Rhinorrhea | 3% | 7% |
- No serious TEAEs in all clinical trials4,6-8
- Most TEAEs were considered mild or moderate and resolved quickly4,6-8
- No risk of needle-related injuries, such as lacerations, finger sticks, or blood vessel injections3,9,10

Not actual size.
*Data include subjects with nasal allergen challenge-induced rhinitis.3
†The trials used a crossover design and, therefore, the total number of subjects do not match the number of unique subjects (n=175).3
‡Two nasal doses of neffy 2.0 mg were administered 10 minutes apart.3
TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
neffy was well tolerated in a robust clinical study program3
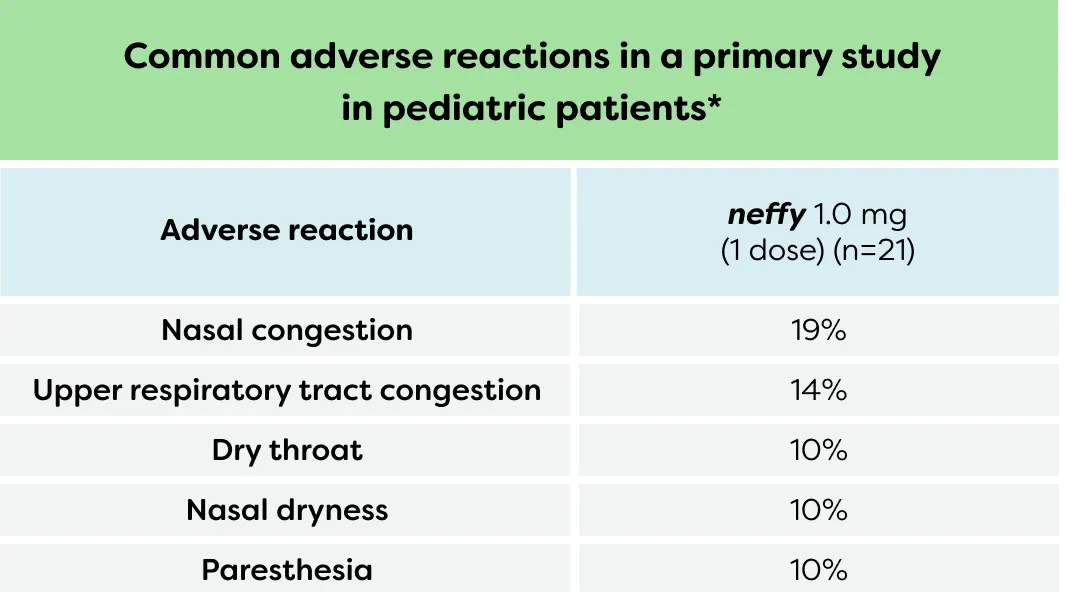
| Common adverse reactions in primary study in pediatric patients* | |
|---|---|
| Adverse reaction | neffy 1.0 mg |
| Nasal congestion | 19% |
| Upper respiratory tract congestion | 14% |
| Dry throat | 10% |
| Nasal dryness | 10% |
| Paresthesia | 10% |


Not actual size.
*Subjects were pediatric patients weighing 15 to <30 kg. The incident of treatment-emergent adverse events shown in the table are for those AEs occurring in ≥2 subjects.3,11
AE, adverse event.
neffy demonstrated a favorable safety profile in pediatric patients,
as well as adults, with no serious adverse events reported in the trials4,5,10
neffy 2 mg primary adult and pediatric studies3,9
| Study | Objectives | Study design | Product, dose, & administration | Patients (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPI 15 | PK and PD of neffy compared to IM and auto-injector injection dosed once and twice | 6-arm, randomized, crossover study | Part 1: neffy 2 mg; 0.3 mg IM; auto-injector 0.3 mg IM Part 2: neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (R/R); auto-injector | Healthy patients (42) |
| EPI 16 | PK and PD of neffy under normal and NAC-induced rhinitis compared to | 4-arm, randomized, partial crossover study | neffy 2 mg; neffy 2 mg w/ NAC-induced rhinitis; | Seasonal allergy patients (36) |
| EPI 17 | PK and PD of neffy with patient self-administration | 2-arm, randomized, crossover study | neffy 2 mg (self-administration); | Type I allergy patients (42) |
| EPI 10 | PK and PD in pediatric type I allergy patients | Single-arm; | neffy 2 mg | Pediatric allergy patients (21) |
| EPI 18 | PK and PD of neffy compared to IM in type I allergy patients with seasonal rhinitis | 5-arm, randomized, crossover study | NAC: neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); 0.3 mg IM twice Rhinitis: 0.3 mg IM twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (R/R) | Type I allergy patients with seasonal rhinitis (41) |
IM, intramuscular; L, left; NAC, nasal allergen challenge; PD, pharmacodynamic; PK, pharmacokinetic; R, right.
References: 1. Casale TB, Spergel JM, Bernstein DI, Tanimoto S. Real-world data on the effectiveness of neffy in clinical practice. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2025. 2. Patel N, Chong KW, Yip AYG, et al. Use of multiple epinephrine doses in anaphylaxis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2021;148(5):1307-1315. 3. neffy [prescribing information]. San Diego, CA: ARS Pharmaceuticals Operations, Inc.
Stay in the know with neffy
Enroll now to get news and updates and learn about programs and resources available to you and your patients.
