- Patients had symptom relief as early as 1 minute2
- Most patients experienced symptom relief within 5 minutes2
- Symptoms resolved in a median time of 15 minutes2‡
- neffy was demonstrated to be safe and tolerable with no serious adverse events observed during the study2,3
PD data
neffy has a rapid effect on heart rate1*†
Effects on heart rate by
epinephrine treatment (After 1 dose)1
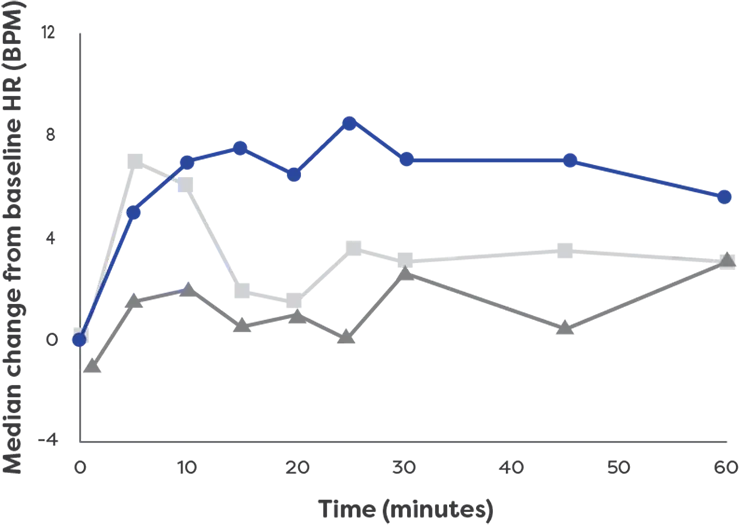
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
neffy had an effect on heart rate within 1 minute
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
*The clinical meaning of PD responses observed in healthy subjects is unclear in the context of treating anaphylaxis.1
†PD analysis of a single dose of neffy
BPM, beats per minute; HR, heart rate; IM, intramuscular; PD, pharmacodynamic.
neffy has a rapid effect on systolic blood
pressure1*†
Effects on systolic blood pressure
by epinephrine treatment (After 1 dose)1
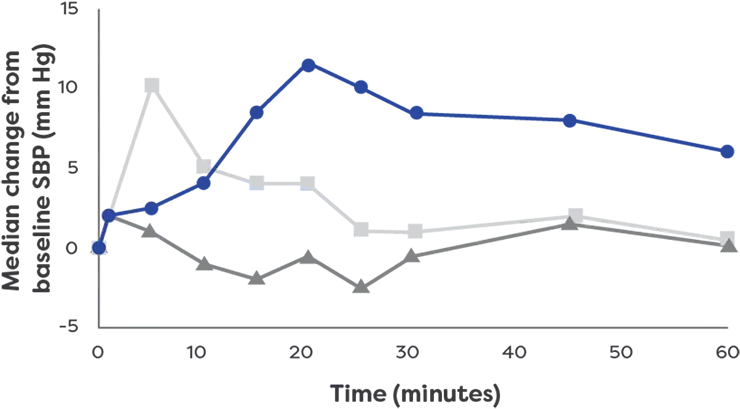
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
neffy had an effect on systolic blood pressure
- neffy 2.0 mg
(n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe) (n=42) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(auto-injector) (n=42)
*The clinical meaning of PD responses observed in healthy subjects is unclear in the context of treating anaphylaxis.1
†PD analysis of a single dose of neffy 2.0 mg compared to
mm Hg, millimeters of mercury; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
100% of patients achieved symptom resolution with 1 dose2
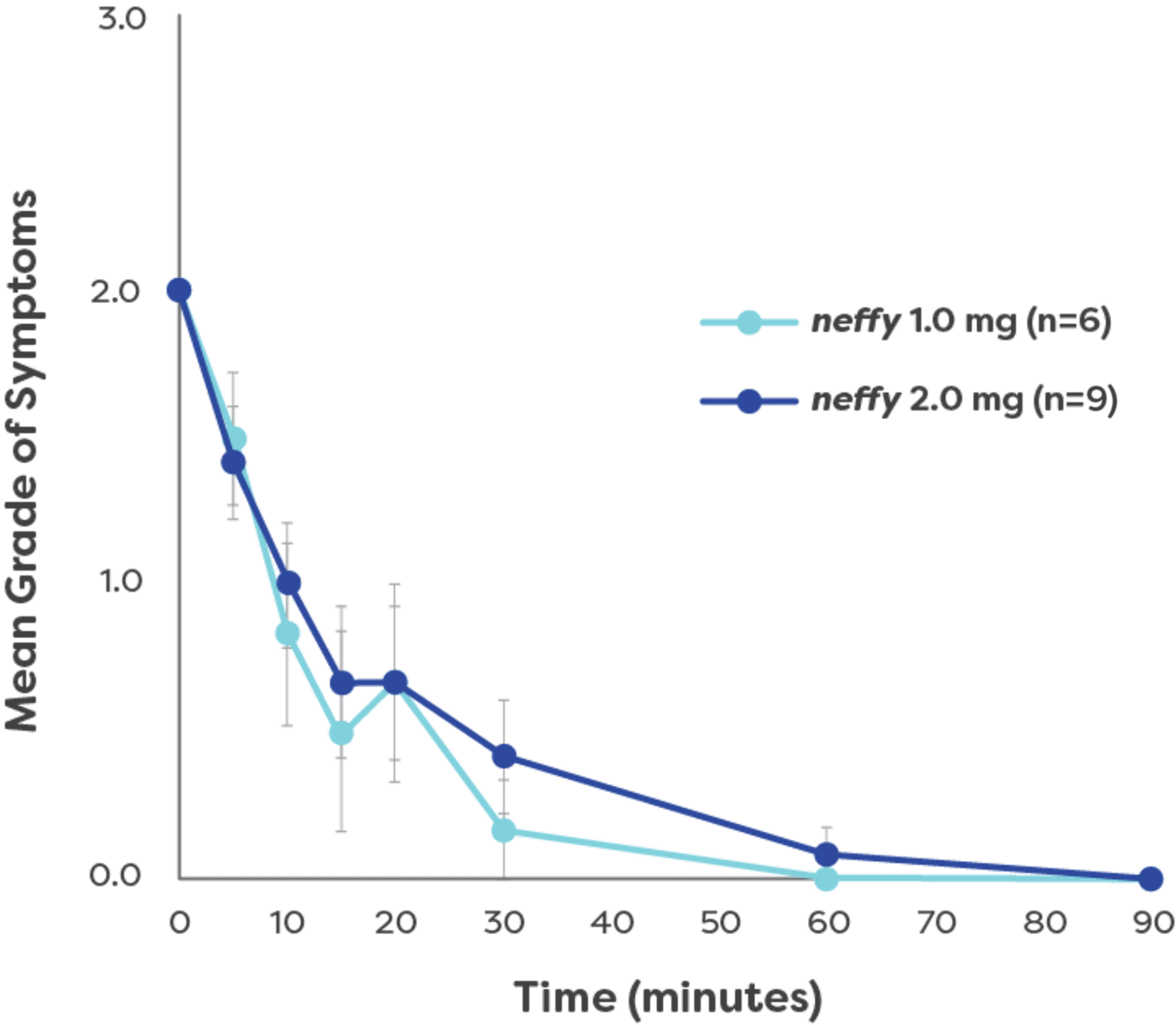
‡One patient developed a biphasic reaction 2 hours and 45 minutes following administration of neffy and was treated with epinephrine at the time of that reaction.2,3
Simulating real-world type I allergic
reactions with OFC
Overview:
This Phase 3, open-label study evaluated the efficacy and safety of a single dose of neffy (
- Clinical symptoms (skin/mucosa, digestive, respiratory, circulatory, nerves) were induced via OFC and graded per the Anaphylaxis Guideline2
- neffy was administered based on weight: 15 to <30 kg:
1.0 mg; ≥30 kg: 2.0 mg2
Patients:
- 15 Japanese pediatric patients (ages 6–17) with confirmed food allergy reactions (Grade 2+ in gastrointestinal, respiratory, or circulatory symptoms)2
Endpoints:
Primary endpoint2:
- Improvement rate from baseline at 15 minutes or before alternative treatment*
(Main symptom prioritization: cardiovascular > respiratory > gastrointestinal)
Selected secondary endpoints2:
- Patients not requiring alternative treatment
- Symptom grade over time
- Time to resolution by organ system
*Improvement was defined as a decrease in the grade of each organ symptom by 1 or more compared to the pre-dose grade.2 Foods that were determined or suspected to be a causative allergen were divided into single doses or multiple doses and were recorded (ie, chicken egg, wheat, milk, peanut, cashew nut, walnut, soba, etc).2
Mild (Grade 1)
- Localized redness, itching, or swelling (lip/eyelid)
- Mild stomach pain, nausea, or single vomiting
- Intermittent cough, nasal congestion, sneezing
Moderate (Grade 2)
- Generalized redness, severe itching, face swelling
- Severe stomach pain, repeated vomiting/diarrhea
- Repetitive cough, wheezing, mild dizziness
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia), mild low blood pressure
Severe (Grade 3) – EMERGENCY
- Widespread swelling, trouble breathing, hoarseness
- Continuous vomiting, loss of bowel control
- Severe wheezing, difficulty swallowing, throat tightness, cyanosis
- Severe low blood pressure, irregular heartbeat, cardiac arrest
- Anxiety, fainting, loss of consciousness
PK data
neffy pharmacokinetic data
neffy remained effective even
in patients with rhinitis1*†
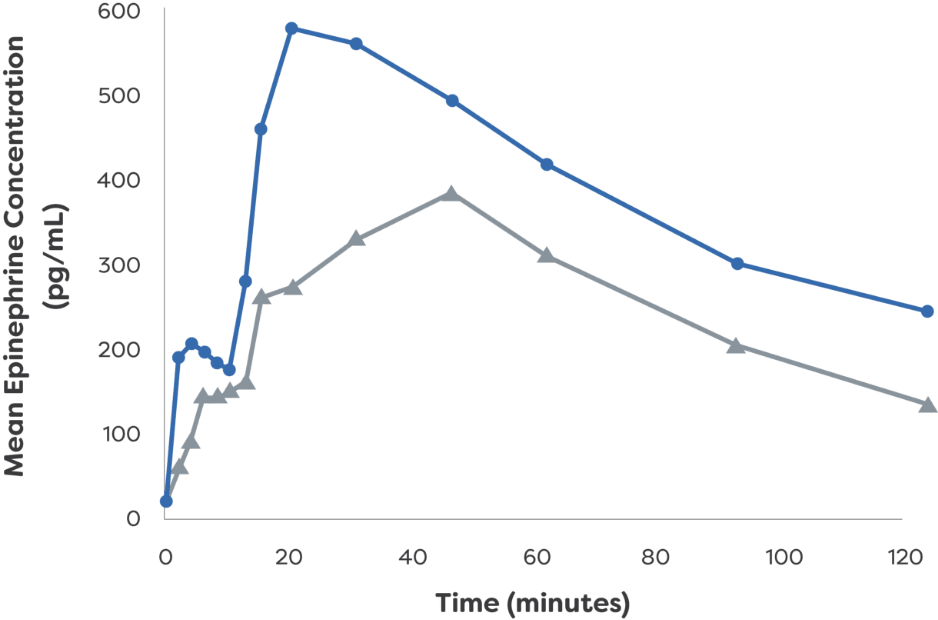
Epinephrine plasma concentration-time profiles following 1 or 2 dose(s) in healthy adults with and without NAC-induced rhinitis1
Mean Epinephrine Concentration: Single Dose1
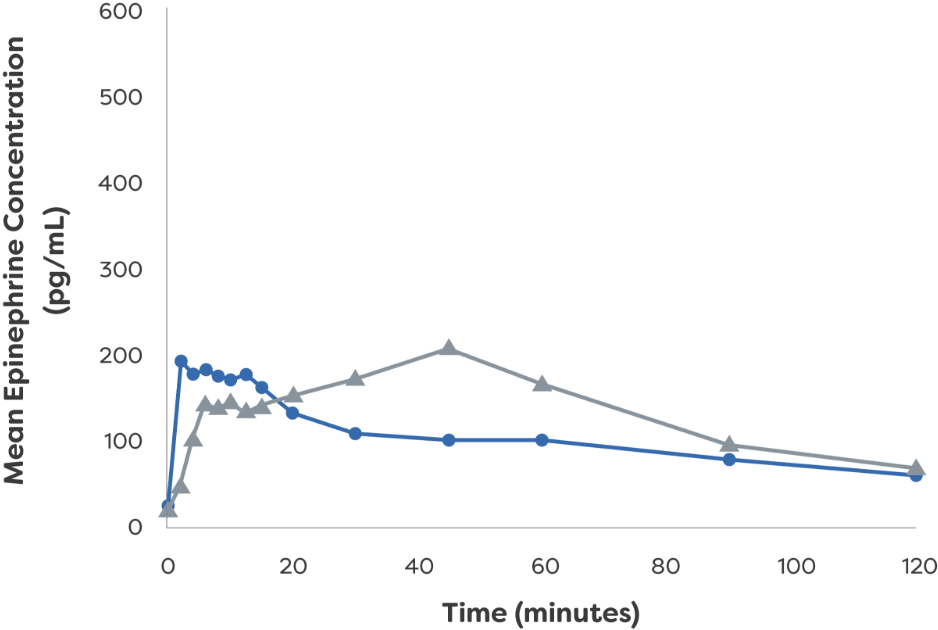
- neffy 2.0 mg
(with NAC) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe)
Mean Epinephrine Concentration: Twice Dose1
- neffy 2.0 mg
(with NAC) - 0.3 mg epinephrine
(needle-syringe)
*PK data are not indicative of efficacy and the clinical significance is not known.1
†Study analyzed PK and PD of neffy
IM, intramuscular; NAC, nasal allergen challenge; PD, pharmacodynamic; pg/mL, picograms per milliliter; PK, pharmacokinetic.
Safety data
neffy was well tolerated in a robust clinical study program1
| Common adverse reactions in primary studies1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse reaction* | neffy 2.0 mg | neffy 2.0 mg |
| Throat irritation | 2% | 19% |
| Headache | 6% | 18% |
| Nasal discomfort | 10% | 13% |
| Feeling jittery | 1% | 11% |
| Tremor | 0% | 8% |
| Rhinorrhea | 3% | 7% |
- No serious TEAEs in all clinical trials2,4-6
- Most TEAEs were considered mild or moderate and resolved quickly2,4-6
- No risk of needle-related injuries such as lacerations, finger sticks, or blood vessel injections1,7,8
*Data include subjects with nasal allergen challenge induced rhinitis.1
†The trials used a crossover design and, therefore, the total number of subjects do not match the number of unique subjects (n=175).1
‡Two nasal doses of neffy 2.0 mg were administered 10 minutes apart.1
TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
neffy was well tolerated in a robust clinical study program1
| Common adverse reactions in a primary study in pediatric patients* | ||
|---|---|---|
| Adverse reaction | neffy 1.0 mg (1 doses) (n=21) | |
| Nasal congestion | 4 (19%) | |
| Upper respiratory tract congestion | 3 (14%) | |
| Dry throat | 2 (10%) | |
| Nasal dryness | 2 (10%) | |
| Paresthesia | 2 (10%) | |
- No serious TEAEs in all clinical trials2,4-6
- Most TEAEs were considered mild or moderate and resolved quickly2,4-6
- No risk of needle-related injuries such as lacerations, finger sticks, or blood vessel injections1,7,8
*Data include subjects with nasal allergen challenge induced rhinitis.1
TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
neffy demonstrated a favorable safety profile in pediatric patients,
as well as adults, with no serious adverse events reported in the trials2,3,8
neffy 2 mg primary adult and pediatric studies1,7
| Study | Objectives | Study design | Product, dose, & administration | Patients (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPI 15 | PK and PD of neffy compared to IM and auto-injector injection dosed once and twice | 6-arm, randomized, crossover study | Part 1: neffy 2 mg; 0.3 mg IM; auto-injector 0.3 mg IM Part 2: neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (R/R); auto-injector 0.3 mg twice | Healthy patients (42) |
| EPI 16 | PK and PD of neffy under normal and NAC-induced rhinitis compared to | 4-arm, randomized, partial crossover study | neffy 2 mg; neffy 2 mg w/ NAC-induced rhinitis; 0.3 mg IM; 0.5 mg IM | Seasonal allergy patients (36) |
| EPI 17 | PK and PD of neffy with patient self-administration | 2-arm, randomized, crossover study | neffy 2 mg (self-administration); 0.3 mg IM (medical staff administration) | Type I allergy patients (42) |
| EPI 10 | PK and PD in pediatric type I allergy patients | Single-arm; | neffy 2 mg | Pediatric allergy patients (21) |
| EPI 18 | PK and PD of neffy compared to IM in type I allergy patients with seasonal rhinitis | 5-arm, randomized, crossover study | NAC: neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); 0.3 mg IM twice Rhinitis: 0.3 mg IM twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (L/R); neffy 2 mg twice (R/R) | Type I allergy patients with seasonal rhinitis (41) |
IM, intramuscular; L, left; NAC, nasal allergen challenge; PD, pharmacodynamic; PK, pharmacokinetic; R, right.
References: 1. neffy [prescribing information]. San Diego, CA: ARS Pharmaceuticals Operations, Inc.
Stay in the know with neffy
Enroll now to get news and updates and learn about programs and resources available to you and your patients.
